The Science Behind Cooking Temperatures
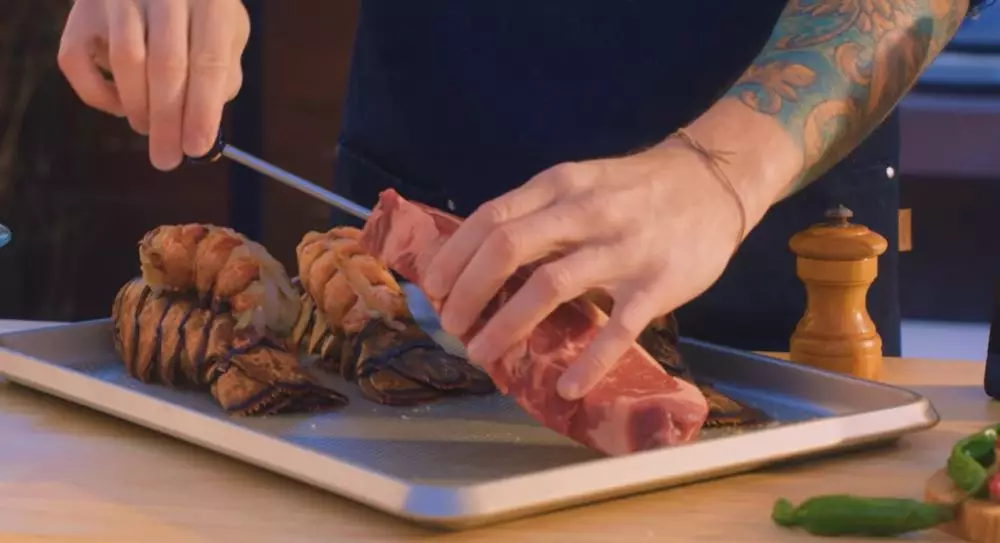
Cooking is both an art and a science. And while creativity and intuition play an important role, precision temperature control is essential to achieving perfectly cooked dishes. Understanding the science behind cooking temperatures can help you elevate your cooking game and create dishes that are not only delicious but also safe to eat. In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind cooking temperatures and explore how the ChefsTemp Finaltouch X10 thermometer can help you achieve perfect results every time.
Table of Contents
The Maillard Reaction
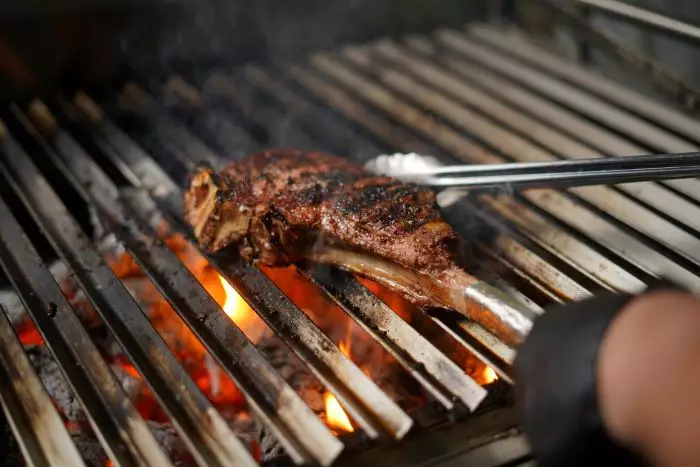
One of the most important concepts in cooking is the Maillard reaction. This chemical reaction occurs when amino acids and sugars are heated together, resulting in the browning and flavoring of food. The Maillard reaction is responsible for the crispy crust on bread, the caramelization of onions, and the sear on a steak. But it’s not just about flavor—the Maillard reaction also plays a key role in food safety.
Food Safety
Food safety is paramount when cooking. The danger zone is the range of temperatures between 40°F and 140°F, where bacteria can grow rapidly and potentially cause foodborne illness. That’s why it’s important to make sure that food stays out of the danger zone for as long as possible. When cooking, it’s best to bring food up to a temperature above 140°F as quickly as possible, and to cool it down rapidly after cooking.
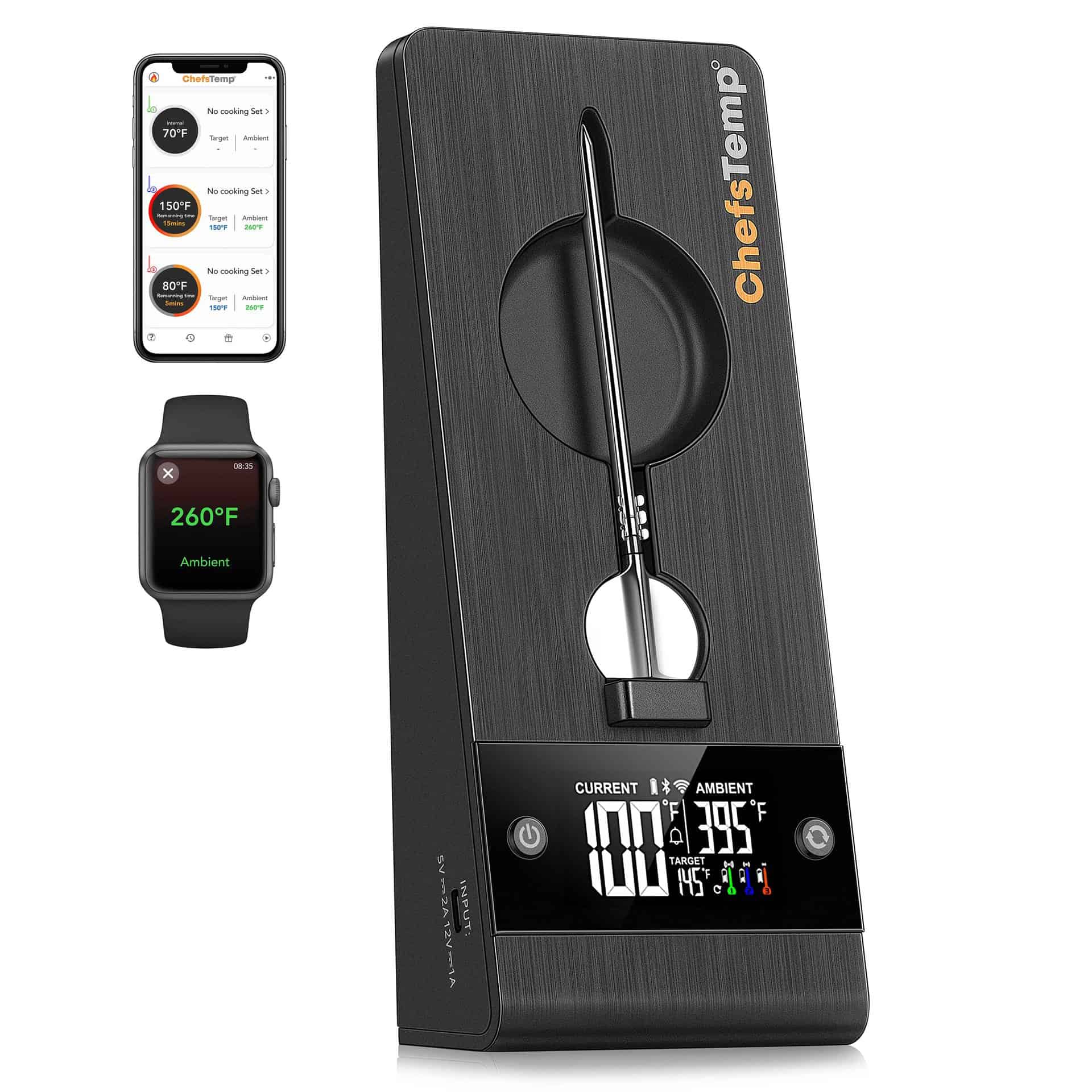
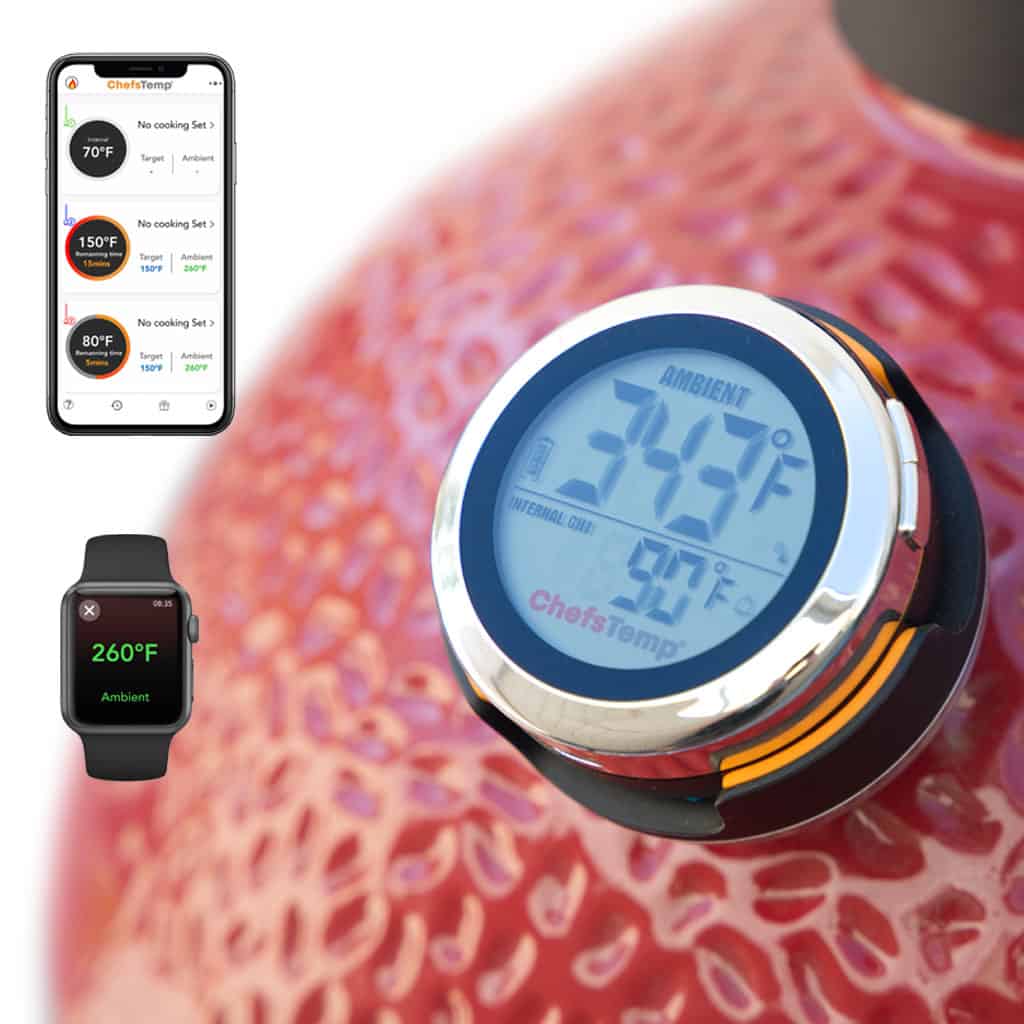
Using the ChefsTemp Finaltouch X10 Thermometer
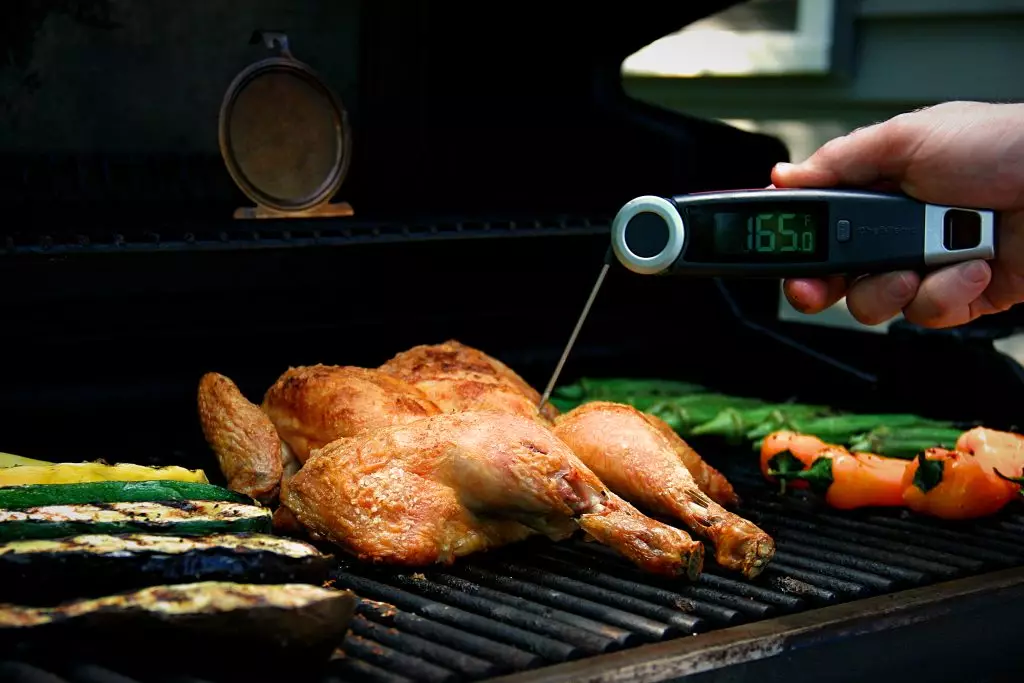
The ChefsTemp Finaltouch X10 thermometer is a high-quality cooking thermometer that allows you to measure the internal temperature of food accurately. It features a stainless steel probe and a large, easy-to-read LCD display, making it easy to use and highly accurate. Different foods require different cooking temperatures to achieve optimal flavor and safety. Here are some guidelines for cooking temperatures for different foods:

- Beef: For rare steak, cook to an internal temperature of 125°F; for medium-rare, cook to 135°F; for medium, cook to 145°F; for medium-well, cook to 155°F; for well-done, cook to 160°F.
- Poultry: Cook chicken and turkey to an internal temperature of 165°F to ensure that they are safe to eat.
- Fish: Cook fish to an internal temperature of 145°F for safety.
- Vegetables: Roast vegetables at 400°F to bring out their natural sweetness and flavor.
- Baked Goods: Different baked goods require different cooking temperatures, but most are cooked between 325°F and 375°F.
The Importance of Resting Meat
Another important concept in cooking is the importance of resting meat after cooking. When meat is cooked, the juices are forced towards the center of the meat. If you cut into the meat immediately after cooking, the juices will flow out, resulting in dry meat. By letting the meat rest for a few minutes before cutting into it, the juices have time to redistribute, resulting in juicier and more flavorful meat.
Conclusion
Understanding the science behind cooking temperatures is essential to achieving perfectly cooked dishes. With thermometer, you can measure the internal temperature of food accurately and achieve perfect results every time. Whether you’re cooking steak, chicken, fish, vegetables, or baked goods, the ChefsTemp Finaltouch X10 thermometer is the perfect tool for achieving precise temperature control and taking your cooking to the next level.
Discover Other ChefsTemp Products
Discover more recipes and learn kitchen tricks by joining our cooking family on Facebook.
You may also like: